
ZEISS Acquires Beyond Gravity’s Lithography Division: Week in Brief: 12/6/24
OBERKOCHEN, Germany, Dec. 6, 2024 — ZEISS has acquired the lithography division of Beyond Gravity, a provider of special actuators and complex mechatronic modules. Located in both Zurich and Coswig, Germany, the company plans to integrate the Coswig site into Carl Zeiss SMT GmbH and will rebrand the Zurich site to Carl Zeiss SMT Switzerland AG. The move expands the ZEISS semiconductor manufacturing technology (SMT) segment’s production and R&D capacities to meet the global demand for semiconductor manufacturing systems, according to the company.

The newly acquired lithography division of Beyond Gravity in Zurich. Courtesy of ZEISS.
BOULDER, Colo. — Quantum information company Infleqtion has received $11 million in funding from the U.S. Department of Defense under the Accelerate the Procurement and Fielding of Innovative Technologies program to support the development of Tiqker, Infleqtion’s rack mounted optical clock. Tiqker will support a range of defense areas, including assured communications, GPS-denied navigation, anti-spoof timing, and synchronization for emerging technologies such as one-way attack drone protection. The project has received a total of $22 million to date.
MUNICH — Satellite communications company Rivada Space Networks has been awarded a contract by the U.S. Navy to engage in joint engineering cooperation with the Navy to delineate a virtual network architecture specifically designed to meet challenges in ship-to-shore and ship-to-ship communications. The cooperation will use Rivada’s Outernet low-Earth orbit satellite constellation, which combines intersatellite laser links with onboard processing to provide routing and switching capabilities to create an optical mesh network in space. Following the award, Rivada launched a new subsidiary named Rivada Secure Services, headquartered in Washington, D.C., to act as a proxy organization to serve the needs of the U.S. government and defense customers.
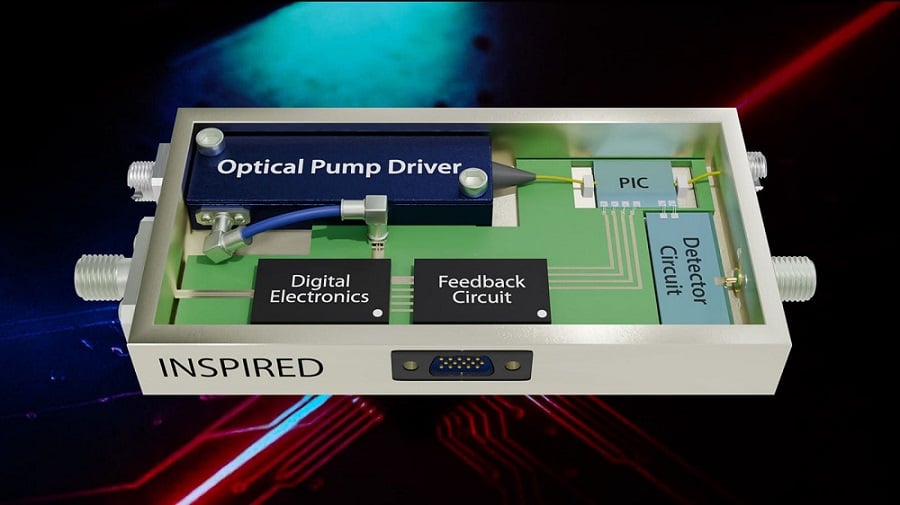
Under DARPA's INSPIRED program, RTX BBN Technologies will develop a prototype photonic chip using quantum states of squeezed light. Courtesy of RTX BBN Technologies.
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. — RTX BBN Technologies, a provider of technology R&D with a focus on national security priorities, has been tapped by DARPA under its Intensity Squeezed Photonic Integration with Revolutionary Detection (INSPIRED) program to develop a prototype photonic chip that uses exotic quantum states of squeezed light to provide users with better awareness of environmental elements critical to their missions. The RTX BBN-led team plans to use its knowledge of photonic integrated circuits and quantum measurement devices to achieve the design and fabrication innovations required to transfer squeezed light capabilities to a fieldable, millimeter-scale detector for detection across a wide frequency range within 100 MHz to 10 GHz.
SAN JOSE, Calif. — Defense and aerospace company BAE Systems has completed environmental testing of NASA’s Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization, and Ices Explorer (SPHEREx) Observatory. SPHEREx will use an advanced imager over its two-year mission to survey the sky in NIR light four times, providing high-resolution color maps of the universe and gathering data on more than 450 million galaxies, along with millions of stars in the solar system. SPHEREx will also work to identify targets of interest for more detailed observation by other satellites, such as the James Webb Space Telescope, and help lay a foundation for future missions like the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope. The mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than February 2025.
LE PLESSIS-ROBINSON, France — MBDA, a missile systems designer, has signed a memorandum of understanding with Leonardo for the joint creation of a laser direct energy weapon. The weapon will use two power classes, depending on the threat, and will be able to intercept and neutralize nano- and micro-drones of different material composition. The intent for the direct energy weapon is for maritime use, with a possible future evolution for land use.
TUCSON, Ariz. — Advanced optical technologies developer Applied Energetics Inc. has signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with defense and aerospace solutions company Kord Technologies to develop and deploy directed energy and pulsed laser technology for defense and national security applications. The MOU outlines areas of cooperation, including joint research and development, integration of specified directed energy technologies into Kord's counter UAS system, and the exploration of opportunities to enhance both companies' product portfolios. This mutual endeavor will also focus on expanding both companies' market presence and establishing a framework for potential future collaborations.
REHOVOT, Israel — Nova, a provider of material, optical, and chemical metrology solutions, has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Sentronics Metrology GmbH, a provider of wafer metrology tools for backend semiconductor fabrication, in an all-cash transaction valued at approximately $60 million. Sentronics Metrology develops flexible and modular metrology tools equipped with multiple metrology sensors for a variety of dimension applications, including thickness, roughness, and topography. The acquisition is expected to close within the first quarter of 2025.
LEEDS, England — Encrypted data processor Optalysys has partnered with open source cryptography company Zama to integrate Zama’s fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) with Optalysys’ hardware acceleration product range, Enable, to expedite FHE adoption for its customers. The partnership aims to bridge the gap in FHE adoption by addressing its historically high computational demands and will allow the use of encrypted data for high-security applications across various sectors.
MONMOUTH JUNCTION, N.J. — Princeton Infrared Technologies, a developer of indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs) imaging technology, has been selected by NASA for a Phase I SBIR contract to develop an advanced 24-bit SWIR imager for the detection of a variety of chemical signatures for atmospheric sensing. The proposed SWIR imager will operate within the 400 nm to 3000 nm wavelength range and is designed to be integrated into a camera with less than 275 electrons of read noise, capable of processing over 250 fps at full resolution and bit depth.
/Buyers_Guide/ZEISS_Industrial_Quality_Solutions/c24905
/Buyers_Guide/Infleqtion/c17990
/Buyers_Guide/Fairchild_Imaging_Inc/c4712
/Buyers_Guide/Applied_Energetics_Inc/c18272
/Buyers_Guide/Princeton_Infrared_Technologies_Inc_PIRT/c25210