Work from the University of Manchester outlines applications for smart surface technology that covers the entire electromagnetic spectrum, including the visible light region. Applications for the new optical devices range from next-generation display devices to dynamic thermal blankets for satellites, as well as multispectral adaptive camouflage.
The tenability of these devices comes from electro-intercalation, a process that in this case involves the interposing of lithium ions between sheets of multilayer graphene (MLG), offering control over electrical, thermal, and magnetic properties.
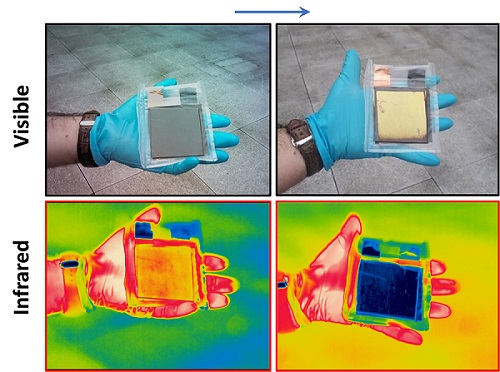
The device on the left is shown in its discharged state, appearing dark gray in the visible spectrum, in contrast to its charged state on the right, where it appears gold in the visible spectrum. Courtesy of the University of Manchester.
The device is laminated and vacuum sealed in a low-density polyethylene pouch that has over 90% optical transparency from visible light to microwave radiation.
The electrical and optical properties of MLG change dramatically between charge, or intercalation, and discharge, or de-intercalation. The discharged device appears dark gray due to the high absorptivity, more than 80%, of the top graphene layer in the visible regime. When the device is fully charged at approximately 3.8 V, the graphene layer appears gold.
The achievable color space can be enriched to include a range from red to blue using optical effects such as thin-film interference.
“We have fabricated a new class of multispectral optical devices with previously unachievable color-changing ability by merging graphene and battery technology,” said Coskun Kocabas, lead author of the study and a professor at the University of Manchester. “The successful demonstration of graphene-based smart optical surfaces enables potential advances in many scientific and engineering fields.”
In the case of a thermal blanket, for example, the device could be tuned to regulate a satellite’s temperature by selectively reflecting visible or infrared light or insulating the satellite from deep-space cooling.
Previous studies on single- and multilayer graphene focused on specific wavelength ranges of microwave, terahertz, infrared, and visible spectra. Extending coverage to visible light while maintaining optical activity at longer wavelengths required innovation in the device’s structure, overcoming difficulties in the integration of optical devices with electrochemical cells.
“Here we used a graphene-based lithium-ion battery as an optical device,” Kocabas said. “By controlling the electron density of the graphene, we are now able to control light from visible to microwave wavelengths on the same device.”
“Few-layer graphene offers unprecedented control over its optical properties through charging,” said Sir Kostya Novoselov, a Nobel laureate and fellow professor and co-author on the research. “Such devices can find their applications in many areas, from adaptive optics to thermal management.”
The research was published in Nature Photonics (www.doi.org/10.1038/s41566-021-00791-1).