
Promising Materials Emerge for Next-Gen LED-Based Data Communications
A team of researchers has examined how organic semiconductors, colloidal quantum dots (CQDs), and metal halide perovskites can be used in high-speed LED-based optical communication systems.
LED-based techniques enable computing devices to communicate with one another by using infrared light. However, LED techniques aren’t often used. In their current state, LEDs transmit data at far slower speeds compared to other wireless technologies such as light-fidelity (Li-Fi).
The team explored efforts to improve the performance and efficiency of these LEDs with consideration of their potential applications in on-chip interconnects and Li-Fi.
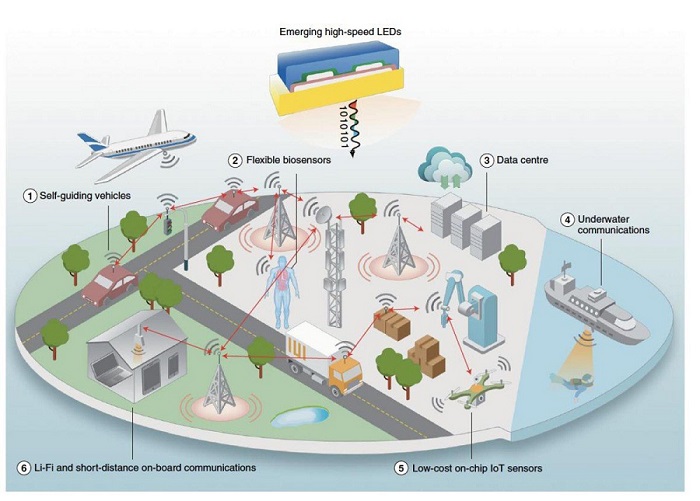
Illustration showing potential applications of next-gen LEDs. Courtesy of the University of Surrey.
“There’s excitement surrounding CQDs and perovskites because they offer great promise for low-power, cost-effective, and scalable communications modules,” said Aobo Ren, co-first author and Ph.D. student at the University of Cambridge. “Although the conventional inorganic thin-film technologies are likely to continue to play a dominant role in optical communications, we believe that LEDs based on these materials can play a complementary role that could have a sizeable impact on the industry.”
According to Hao Wang, co-first author and Ph.D. student at the University of Cambridge, LEDs will no longer be limited to lighting and displays.
“The development of LEDs based on these solution-processable materials for optical communication purposes has only begun, and their performance is still far from what’s required,” Wang said. “It is necessary and timely to discuss the potential strategies and present technical challenges for the deployment of real-world communication links using these LEDs from the material, device, and system aspects.”
Jiang Wu, corresponding author and a professor at the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China noted that photonic systems for the Internet of Things and 6G will need to be fast, easy to integrate, and low cost.
“Organic semiconductors, CQDs, and perovskites are promising materials that could be used to complement and/or compete with conventional inorganic counterparts in particular optoelectronic applications,” Wu said.
The research was published in Nature Electronics (www.doi.org/10.1038/s41928-021-00624-7).
Published: September 2021