Researchers from Leibniz University Hannover, the University of Twente, and photonic quantum computing company QuiX Quantum have presented an entangled quantum light source fully integrated on a chip. According to team member Michael Kues, who is head of the Institute of Photonics and a board member of the Cluster of Excellence PhoenixD at Leibniz University Hannover, the breakthrough enabled the researchers to shrink the source size by a factor of more than 1000.
Among other benefits that include reproducibility, stability, and scaling, the achievement supports the potential for mass-production, Kues said.
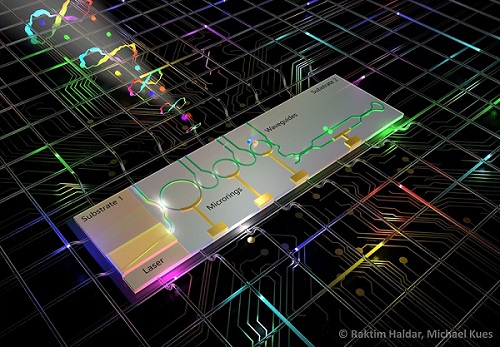
Illustration of the chip-integrated quantum light source for the generation of entangled photons. Courtesy of Raktim Haldar and Michael Kues.
Quantum light sources have, until now, required external off-chip, bulky laser systems, which has limited their use in the field. Previously, said Raktim Haldar, a Humboldt fellow in Kues’ group, it was a major challenge to integrate a laser, filter, and cavity on the same chip due to the lack of a material that was efficient to use to build these different components.
The hybrid technology comprises an indium phosphide laser, a filter, and a cavity made of silicon nitride. On the chip, in a spontaneous nonlinear process, two photons are created from a laser field. Each photon spans a range of colors simultaneously, called “superposition,” and the colors of both photons are correlated; that is, the photons are entangled and can store quantum information.
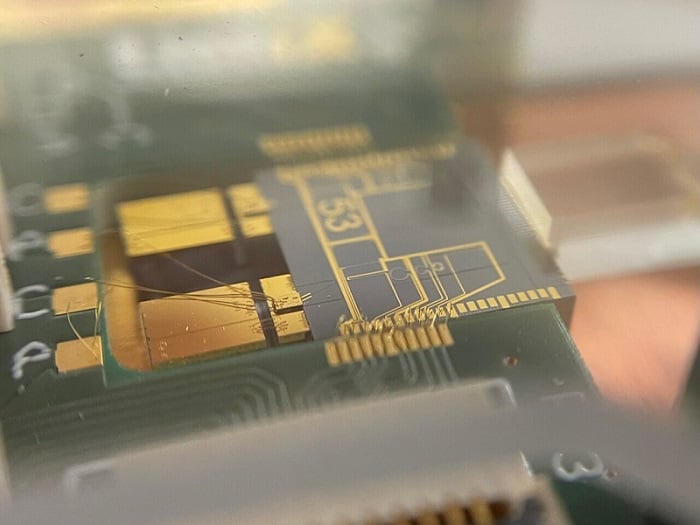

The whole quantum light source fits on a chip smaller than a euro coin. The researchers reduced the size of the light source by a factor of more than 1000 by using a novel, hybrid architecture that combines a laser made from indium phosphide and a filter made of silicon nitride on a single chip. The light source is efficient and stable and can find applications to drive quantum computers or the quantum internet. Courtesy of the Institute of Photonics/Leibniz University of Hannover.
According to Haldar, unlike Google, for example, which he said currently uses supercold qubits in cryogenic systems, a quantum advantage could be achieved via the recent work, with a photonic system on a chip even at room temperature.
The researchers expect that the work will help to lower the production costs of applications.
“We can imagine that our quantum light source will soon be a fundamental component of programmable photonic quantum processors,” Kues said.
The research was published in Nature Photonics (www.doi.org/10.1038/s41566-023-01193-1).