The properties and performance of semiconductor chips powering modern technologies are ultimately determined by free electrons. With the continued miniaturization of electronic and photonic devices, tools to examine the behavior of free electrons, simultaneously at the picosecond-time and nanometer-length scales, have become necessary.
A method developed by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley is poised to allow more effective measurement of these electrons, opening paths to better energy efficiency. The researchers developed what they described as a new type of optical nanoscopy to measure electron dynamics in semiconductors.
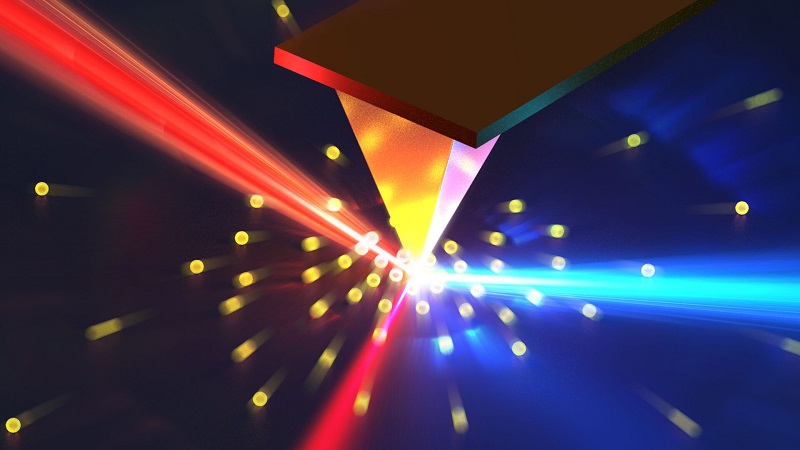
Optical nanoscopy uses laser beams to strike free electrons, scattering light and providing insights into electron distribution and dynamics within semiconductor materials. Courtesy of Laser Thermal Lab/UC Berkeley.
“Our optical nanoscopy integrates near-field scanning optical microscopy and pump-probe optics to enable high resolution at both spatial and temporal scales,” said Costas Grigoropoulos, professor of mechanical engineering and principal investigator of the study. The technology can be applied to a range of semiconductor materials, including silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide, as well as other exotic materials, such as 2D materials and ferroelectrics, he said.
The technique uses a combination of optical imaging and laser probing technologies to measure electrons at picosecond and nanometer scales. Using ultrafast lasers and an atomic force microscope (AFM) tip with an apex curvature of less than 30 nm, the researchers shine two laser beams — a pump beam followed by a probe beam — onto the AFM tip. The first beam excites electrons in the sample, and after a carefully timed delay, the second beam strikes the tip. The local information on electron properties can then be obtained by analyzing the scattered light of the second beam.
Using the method, the researchers bypassed the optical diffraction limit, said Jingang Li, lead author of the study and a postdoctoral scholar in the Grigoropoulos lab. “Therefore, we can demonstrate an improvement in the spatial resolution from several hundred nanometers (for conventional pump-probe microscopy) to 35 nm (for our near-field pump-probe nanoscopy). Such nanoscale resolution enables the measurement of local carrier dynamics in many heterogeneous materials and nanodevices.”
According to Li, the method’s high temporal and spatial resolution enable it to probe carrier dynamics in many emerging materials systems, including phase transitions such as those in vanadium dioxide, defects and quantum emitters, doping sites, and edge states in 2D materials, among others.
The measurements could inform advancements in energy efficiency and other properties.
“With a high density of chips in integrated circuits, the electron distribution and transport not only control the device functionality, but also govern the heat generation and dissipation process,” Li said. “Our nanoscopy will enable the investigation of nanoscale thermal management in these densely packed devices.”
The next step is to validate the technique’s applicability to optoelectronic devices such as photodetectors, Li said.
The research was published in Nano Letters (www.doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c04790).