CEA-Leti and CEA-Irig have developed a lensless imaging technology capable of identifying bacteria with more than 95% accuracy. The device aims to address the problem of antimicrobial resistance, which is an increasing public health problem. According to the World Health Organization, drug-resistant diseases will cause 10 million deaths annually by 2050 if a solution to the problem is not introduced.
The device introduced by the CEA is at least 10× less expensive than an optical microscope designed for similar purposes, and it can analyze up to 10,000 biological objects at a time.
Lens-free scheme. Courtesy of CEA.
The device illuminates bacterial colonies with a semicoherent light source, scattering the light into a unique optical signature that is then analyzed to identify the strain. Specifically, the diffraction pattern characteristics of each strain are recorded on a CMOS sensor and then analyzed by artificial intelligence algorithms. When a database of lab strains is used, the algorithms are more than 95% accurate. Their performance will improve as they encounter a wider variety of samples.
Mass spectrometry techniques typically used for bacterial identification require expensive equipment, which can be a barrier for adoption in countries with impeded development.
In research for the EU Simble project, the CEA is adapting the technology for use in sub-Saharan Africa. The device will be modified to withstand exposure to dust and moisture and will be able to operate off an unstable power supply. The technology is expected to be deployed in Burkina Faso and Benin.
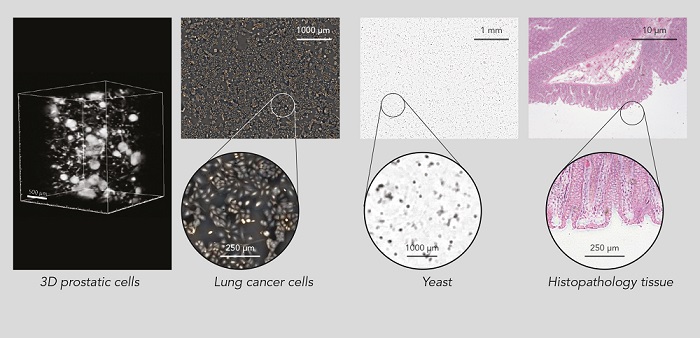
The CEA-Leti lens-free imaging technique, using only generic hardware, can be adapted to different medical diagnostics by developing specific data-processing chains for tests. These tests include a complete blood count test, which CEA-Leti said it developed in partnership with Horiba meningitis screening from spinal fluid, developed in partnership with Marseille-Méditerranée University Medical Center; and a blood coagulation test, developed in partnership with startup Avalun. Other health care applications cited by CEA-Leti for the technique include the monitoring of bioprocesses in bioreactors for the pharmaceutical industry and 2D imaging for standard biological research and drug screening.