
Cognata, Partners Bring Digital Twin-Based Simulation into Microsoft Azure
Autonomous driving technologies developer and computer vision company Cognata will collaborate with Microsoft on its Automated Driving Perception Hub (ADPH) global program. The program, which will run on Microsoft Azure, aims to enable automotive customers to virtually and efficiently evaluate advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS)/autonomous vehicle (AV) sensors through digital twin-based sensor simulation.
Cognata's ADPH allows sensors to be evaluated against a common set of industry-standard scenarios, and their performance to be analyzed quickly and easily. The platform incorporates accurate, manufacturer-approved sensor modeling with a wide spectrum of sensors, such as RGB cameras, with varying lens distortions, point-cloud lidar systems, and infrared thermal cameras all integrated with a deep neural network-based photorealistic layer.
The program technology will additionally incorporate EPYC processors — provided by semiconductor company AMD — and graphics processing units from Radeon.
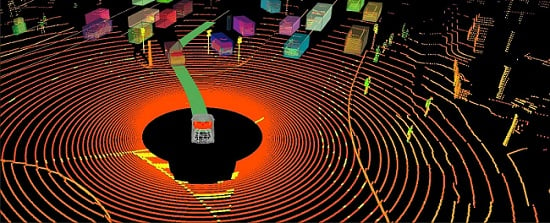
A visualization of Cognata’s advanced sensor viewer. Courtesy of Cognata.
In a separate announcement, Lidwave, a developer of lidar-on-a-chip sensors, said this week that its MonoStaticOne sensor is available for simulation of industrial and automotive use cases on Cognata's perception hub. The two companies will hold a joint technology demonstration at CES 2024 in Las Vegas next week.
/Buyers_Guide/Lidwave_Ltd/c33589