Photonics HandbookThe News Wire
CEA-Leti Reports Progress on AI-Embedded CMOS Image Sensors
CEA-Leti researchers reported success in three related projects that are key steps to enabling a new generation of CMOS image sensors that can exploit all the image data to perceive a scene, understand the situation, and intervene in it — capabilities that require embedding AI in the sensor.
Demand for smart sensors is growing rapidly due to their high-performance imaging capabilities in smartphones, digital cameras, automobiles, and medical devices. This demand for improved image quality and functionality enhanced by embedded AI has presented manufacturers with the challenge of improving sensor performance without increasing the device size.
“Stacking multiple dies to create 3D architectures, such as three-layer imagers, has led to a paradigm shift in sensor design,” said Renan Bouis, lead author of the paper, "Backside Thinning Process Development for High-Density TSV in a 3-Layer Integration."
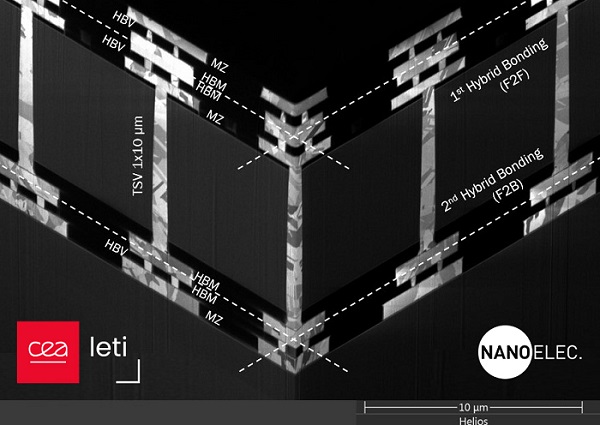
Focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy 3D cross-section of the entire test vehicle structure. The pitch is 6μm for the hybrid bonding pads and HD TSV dimensions are 1x10μm. Courtesy of CEA-Leti.
Communication between the different tiers, he said, necessitates advanced interconnection technology. This requirement is met by hybrid bonding due to its very fine pitch in the micron and sub-micron range. “High-density through silicon via (HD TSV) has a similar density that enables signal transmission through the middle tiers. Both technologies contribute to the reduction of wire length, a critical factor in enhancing the performance of 3D-stacked architectures,” Bouis said
The three projects, presented at ECTC 2024, applied the institute's previous work on stacking three 300 mm silicon wafers using those technology bricks.
“The papers present the key technological bricks that are mandatory for manufacturing 3D, multilayer smart imagers capable of addressing new applications that require embedded AI,” said Eric Ollier, project manager at CEA-Leti and director of IRT Nanoelec's Smart Imager program. The CEA-Leti institute is a major partner of IRT Nanoelec.
“Combining hybrid bonding with HD TSVs in CMOS image sensors could facilitate the integration of various components, such as image sensor arrays, signal processing circuits and memory elements, with unparalleled precision and compactness,” said Stéphane Nicolas, lead author of the paper, 3-Layer Fine Pitch Cu-Cu Hybrid Bonding Demonstrator With High Density TSV For Advanced CMOS Image Sensor Applications.
The project developed a three-layer test vehicle that featured two embedded Cu-Cu hybrid-bonding interfaces, face-to-face (F2F) and face-to-back (F2B), and with one wafer containing high-density TSVs.
Ollier said the test vehicle is a key milestone because it demonstrates both feasibility of each technological brick as well as the feasibility of the integration process flow.
“This project sets the stage to work on demonstrating a fully functional three-layer, smart CMOS image sensor, with edge AI capable of addressing high performance semantic segmentation and object-detection applications,” he said.
At ECTC 2023, CEA-Leti scientists reported a two-layer test vehicle combining a 10-μm high, 1-μm diameter HD TSV and highly controlled hybrid bonding technology, both assembled in F2B configuration. The recent work then shortened the HD TSV to 6-μm high, which led to development of a two-layer test vehicle exhibiting low dispersion electrical performances and enabling simpler manufacturing.
According to Stéphan Borel, lead author of the paper, "Low Resistance and High Isolation HD TSV for 3-Layer CMOS Image Sensors," CEA-Leti’s 1×6 μm copper HD TSV provides better electrical resistance and isolation performance compared to their 1×10 μm HD TSV. This, he said, is owed to an optimized thinning process that allowed the substrate thickness to be reduced with favorable uniformity.
“This reduced height led to a 40 percent decrease in electrical resistance, in proportion with the length reduction. Simultaneous lowering of the aspect ratio increased the step coverage of the isolation liner, leading to a better voltage withstand," he added.
According to Ollier, the results establish CEA-Leti as a global leader in the field of next-generation smart imagers. The technology is expected to enable a variety of new applications.
/Buyers_Guide/CEA-Leti/c24495